Knowledge - Mon, 12/09/2024 - 11:21
What Pregnant Women Should Know About Epidural Analgesia For Labor
Last update 12/09/2024 - 11:22
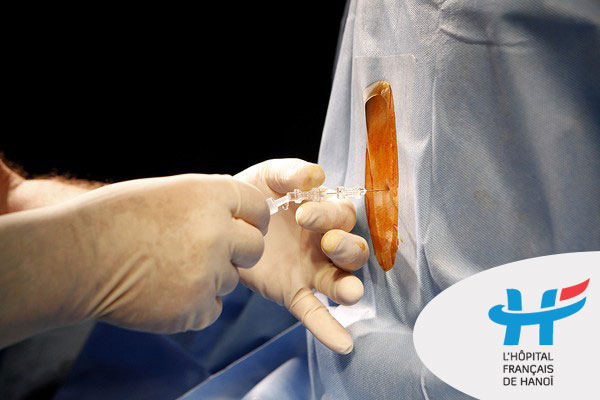
What is epidural anesthesia?
Epidural anesthesia is a type of regional anesthesia applying to relief the pain during labor, to manage post-operative pain, to make pain-free during cesarean section and some other surgeries.
Regional anesthetic is injected into a space surrounding the medulla, called “epidural space”. In epidural analgesia for labor pain relief, after the first manual bolus dose given by an anesthestist, regional anesthetic will be either continuously delivered by an electric pump at low rate until your baby is born, or you will control the pain by yourself whenever you need by pressing a button provided (PCEA), or the electric pump will programmed intermittently deliver a pre-set bolus dose (PIEB). By this way, pregnant women will suffer less pain, the labor will become less stressful, faster, more comfortable and therefore the baby will have less trauma.
Epidural analgesia procedure is performed by experienced anesthetists.
How epidural analgesia is performed?
You will meet anesthetist in pre-anesthesia consultation, he or she will tell you what should do to prepare for the epidural analgesia for labor in near future. Usually the epidural analgesia will be performed when real labor happens. It means that when you have already significant periodical abdominal pain due to rhythm uterus contraction.
Before this procedure, you will be given IV drip to minimize hypotension from anesthetic. Then you will be asked to sit up or lie on the side with your back maximum bended, the chin tucked into the chest. Anesthetist will make local anesthesia where the needle will puncture at your back, so during this procedure you will have almost no pain. Then a plastic tube small as a hair called “epidural catheter” will be inserted into your epidural space. This catheter is so tiny that you can lie comfortably without unhindered.
What you may fill when epidural analgesia procedure is performing?
At the first step of the procedure, in a sitting or lying at a side position, you will be anesthetized at the puncture site. You will feel some light pain at your back as any other injection pain. When the anesthetic is injecting via catheter, you may feel a cool stream flowing along your back. Few minutes after epidural anesthetic injection, you should feel the pain relief progressively. The sensation may vary from one to others depending on the individual feeling. For example, some may experience warm feeling at their feet, others talk about the numbness like ant crawling in the foot, or simply have a feeling of heaviness in their legs, ... These feelings are sometimes uneven between the left and the right.
You should tell anesthetist or midwife whatever you feel.
What benefits at doing epidural analgesia?
Epidural analgesia helps you to avoid the "pain as the pain at delivery» when you are in labor and deliver your baby. Thanks to epidural analgesia, the labor and the childbirth become easier, you will feel more comfortable at each stages of delivery and therefor you can save your energy. If you had been afraid of pain in your previously childbirth, with the epidural analgesia this time, you should worry and scare of nothings.
Thank to epidural analgesia, your obstetricians can conduct your labor and delivery in the best way for both of you and your baby.
In case of instrumental delivery like vacuum or forceps assistant needed, or in case of episiotomy repair, cervical verification after delivery, ..., the epidural analgesia provides good pain management for most of the cases.
If you need an emergency cesarean section, anesthetist can use the available epidural catheter for anesthesia for pain-free during surgery and for postop pain management.
Has epidural analgesia any harm to pregnant women and their fetus?
Epidural analgesia is a medical procedure. Like other medical procedures, besides the obvious benefits, epidural analgesia also has some disadvantages and certain complications.
Anesthetics may cause vasodilatation, hypotension and can affect blood supply to the fetus. Some women may experience nausea, sweating, weakness or difficult breathing due to hypotension. To avoid this phenomenon, you will receive intravenous infusion before epidural analgesia. During epidural analgesia course, your pulse and blood pressure as well as your fetal heart rate and uterine contractions are continuously monitored by a specific obstetric monitoring.
Uterine contractions may somewhat be affected by anesthetics, by tracking the frequency and intensity of uterine contractions in this obstetric monitoring, obstetricians and midwives will know exactly when and how to manage the uterine contractions using medications.
Epidural analgesia had been demonstrated not to increase the rate of cesarean section or instrumental delivery.
After delivery, some women report discomfort in their back, but this feeling usually in the pregnant women who even do not make epidural anesthesia. Researches had confirmed that there is no relation between postpartum chronic backache and epidural analgesia.
Rare complications:
Following epidural analgesia, some woman may have headache for several days, sometimes it is a terrible pain. In theory, this headache will reduce and disappear after a few days without treatment and without sequela. However, doctors will use medications, infusion… and advise the women what to do (lying down, more water intake, relaxing ...) to treat the headache. If these methods do not relieve the headache, a method called "blood patch" will be performed. Anesthesiologists will take approximately 20 ml blood from the women’s vein then inject into her epidural cavity to «seal» the dural puncture. To minimize the complication, women is required to stay still during the time when epidural analgesia is performing.
Epidural cavity infection is a serious complication which may occur. Women will have increasing back pain after childbirth, signs of infection together with neurological signs in the legs. Well respect the sterile technic will minimize this complication. Medical literatures have also reported epidural hematoma following epidural anesthesia. However, these complications are rare (0.04%, http: //www.healing-arts.org/mehl-madrona/mmepidural.htm#intro). Even it happens, lumbar MRI or CT-scan will give accurate diagnosis to guide effective treatment.
Which pregnant women can get epidural analgesia for labor?
Pain tolerance is an individual feeling. It varies from one to others, but most of them feel the labor softer if epidural analgesia was provided. If you want to have epidural analgesia for your labor, and if you have been examined by an anesthetist, he or she will tell you if you can get it.
Which pregnant women should not get epidural analgesia for labor?
Epidural anesthesia should not be performed in those with a history of coagulopathy, severe thrombocytopenia, a history of certain neurological diseases, signs of general infection, or back skin infection at the puncture site, … Anesthetist will decide to do epidural analgesia for a pregnant women or not.
Epidural anesthesia should be done at the right time, when indicated. When the cervix has almost full dilated, there will be not enough time to realize it and the effect of epidural analgesia is quite limited.
Epidural analgesia is also not indicated in emergency situations where the life of the mother or child is threatened, like severe bleeding or fetus failure…
Labor and delivery are difficult periods, but it is also a great moment in your life to welcome your expected baby. With epidural analgesia, we'll help you to get through it comfortable and safe. However, epidural analgesia is not obligatory, the normal delivery does not depend on it. Epidural analgesia for labor is your choice.
For further information of the First class maternity packages, please contact us via HOTLINE 024.35771100 or INBOX FANPAGE "Hanoi French Hospital" or Zalo OA zalo.me/2008009049335817955 or send us an inquiry in the form below: